Mysterious Drones in the U.S: Security risks, Legal loopholes, and Media controversy
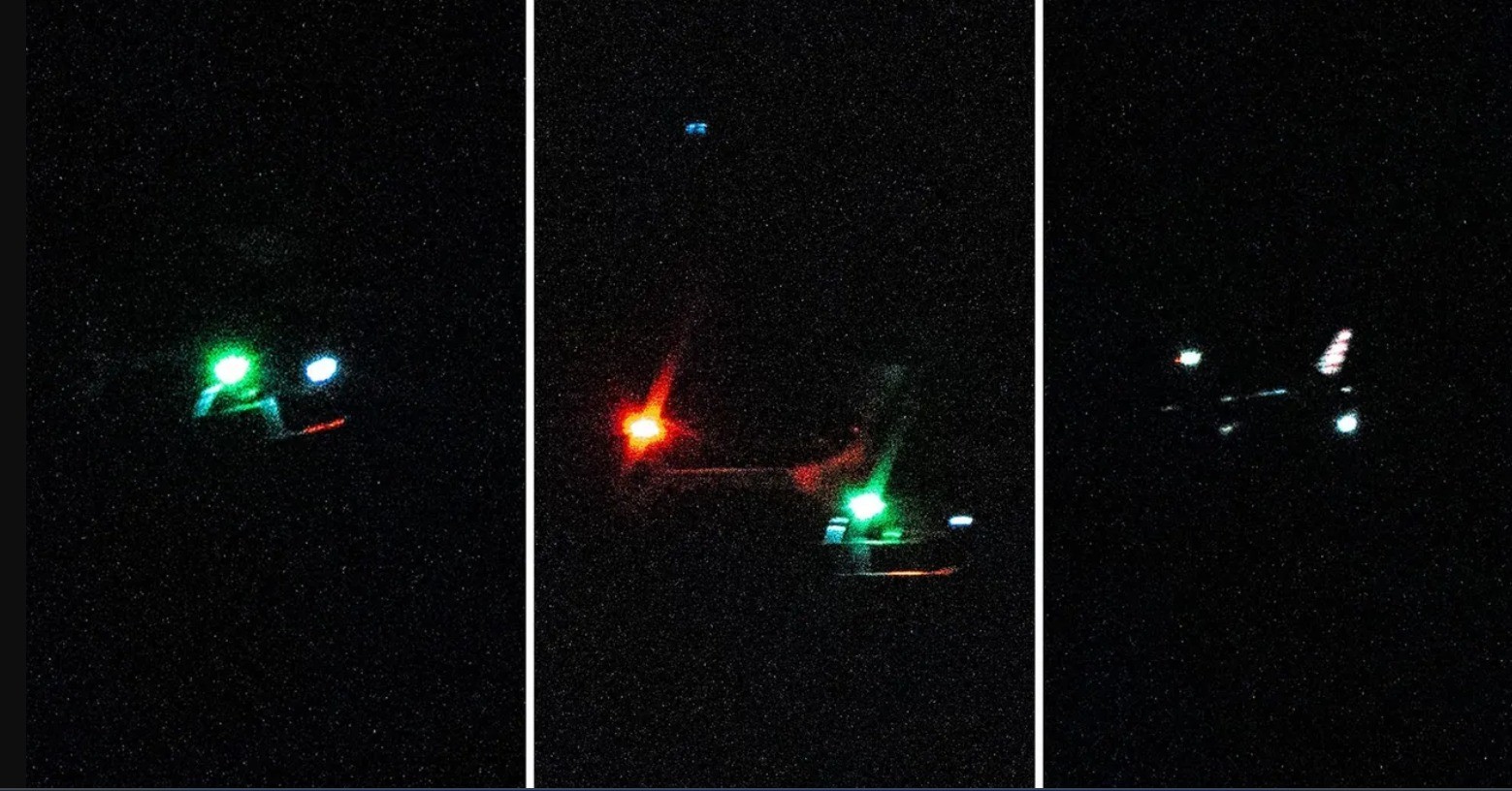
These drones, often described as highly advanced and capable of long-range operations, have been sighted near sensitive locations, such as nuclear facilities, military bases, and critical infrastructure. While many incidents remain unsolved, suspicions have grown that some of these drones could be connected to foreign actors, especially China, raising alarms about espionage and surveillance.
 |
This phenomenon has ignited debates about security vulnerabilities, legal challenges in counter-drone measures, and media-driven controversies surrounding the incidents. Are these drones merely a domestic issue caused by hobbyists or private operators, or do they represent a new frontier in state-sponsored intelligence warfare?
The Growing Threat of Unidentified Drones
1. Sightings and Incidents
Reports of mysterious drone activity have surged since 2019. Key examples include:
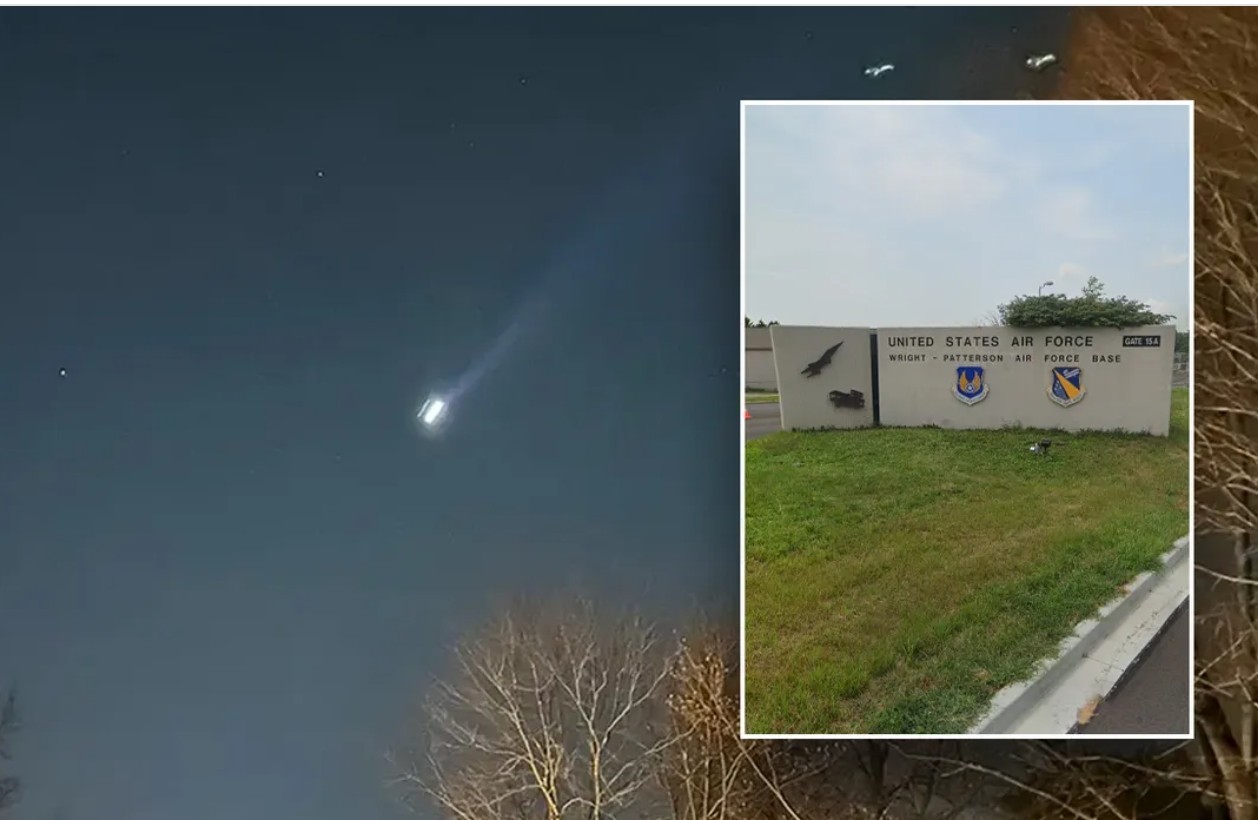
- Nuclear Facility Incidents (2019): A group of drones was spotted flying in formations near nuclear missile silos in Colorado and Nebraska, staying in the air for hours without identification.
- Naval Ship Encounters (2021): U.S. Navy warships near California reported being followed by swarms of drones operating beyond normal commercial capabilities.
- Airports and Critical Infrastructure (2023): Unidentified drones disrupted operations at multiple U.S. airports, leading to temporary shutdowns and public safety concerns.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) reported that drone-related incidents near restricted airspace increased by 67% from 2021 to 2023, indicating a troubling trend.
2. Espionage Concerns and Links to China
Some experts believe that these drones may be part of state-sponsored surveillance programs, with China being a primary suspect:
- Technological Capabilities: Chinese-made drones, such as those produced by DJI (Da Jiang Innovations), dominate the global market, with an estimated 75% of consumer drones sold in the U.S. being Chinese-made. Their widespread use raises concerns about data being transmitted back to foreign servers.
- Espionage Allegations: In 2021, the U.S. Department of Defense flagged Chinese drones as potential security risks. Some reports claim that drones operating near U.S. military installations exhibit flight patterns and technical features consistent with foreign reconnaissance missions.
While no direct evidence links every unidentified drone to China, the sheer volume of advanced drone sightings has led intelligence agencies to explore this possibility seriously.
 |
3. Technological Risks
Modern drones are equipped with sophisticated technology that enables:
- Long-Range Surveillance: High-definition cameras, thermal imaging, and radar can capture sensitive data from miles away.
- Jamming and Disruption: Some drones are capable of interfering with communication networks or GPS signals.
- Weaponization: While rare, drones can be modified to carry small explosives or conduct physical attacks, posing direct threats to public safety.
The U.S. Department of Homeland Security has identified drones as a growing challenge in domestic terrorism, espionage, and cyber warfare.
Legal Loopholes: Why Drones Are Hard to Stop
1. Federal Restrictions on Shooting Down Drones
Under federal law, shooting down or interfering with drones is prohibited, even if they enter private property. This is because drones are classified as aircraft under FAA regulations, and destroying them could result in fines or criminal charges.
2. Legal Gaps in Counter-Drone Technology
Although the U.S. military has advanced counter-drone systems, deploying such measures in civilian areas is highly restricted:
- Civilian Use Prohibited: Anti-drone technologies like jamming systems and net guns are often illegal for private citizens and local law enforcement.
- Lack of Clear Protocols: In cases of unidentified drones near critical infrastructure, there is no unified federal protocol for immediate response.
3. State vs. Federal Jurisdiction
State governments have limited authority to regulate drones because airspace is federally controlled. This creates challenges for local officials trying to address drone incidents quickly.
Read More: What Is the Origin of the Drones Over U.S. Skies? Investigation Limits and the Military Perspective
Media Controversy and Public Perception
The media has played a significant role in shaping public opinion about mysterious drones. However, coverage has often been polarized:
- Alarmist Reporting: Some outlets portray drones as existential threats, focusing on espionage and terrorism angles. Headlines like “Are Chinese Drones Spying on America?” fuel fears without providing concrete evidence.
- Skepticism: Others argue that most drones are likely operated by hobbyists, corporations, or research organizations, downplaying the security risks.
Public opinion is divided. A 2024 survey by Pew Research Center found that 63% of Americans believe drones pose a national security threat, while 25% believe the threat is exaggerated.
Potential Solutions and Policy Recommendations
1. Strengthening Drone Regulations
- Require advanced remote identification systems for all drones, allowing authorities to trace ownership and origin in real time.
- Implement stricter licensing for drone operators, particularly those flying near sensitive areas.
2. Expanding Counter-Drone Measures
- Invest in non-lethal counter-drone systems for local law enforcement, such as signal jammers or interception drones.
- Develop legislation allowing private property owners to neutralize drones under certain circumstances, such as trespassing or surveillance.
3. Enhancing Public Awareness
Educating the public about responsible drone use can reduce accidental violations of restricted airspace while encouraging reporting of suspicious activity.
4. International Collaboration
Work with allies to address the global implications of drone surveillance and prevent foreign adversaries from exploiting U.S. airspace.
Comparisons to Other Countries
Countries like Israel and the UK have implemented more aggressive anti-drone measures, providing useful models:
- Israel: Uses systems like Iron Dome to intercept hostile drones. Israel has also pioneered drone-jamming technologies for use in civilian areas.
- UK: In 2020, the UK deployed anti-drone teams equipped with radio-frequency disruptors during public events.
By adopting similar strategies, the U.S. could close many of its current security gaps.
FAQs
1. Are drones over U.S. airspace always foreign?
Not necessarily. While some drones may be linked to foreign governments or companies, many are operated domestically by hobbyists, researchers, or businesses.
2. Can drones be legally shot down?
No. Under current U.S. law, shooting down a drone is illegal unless authorized by the federal government.
3. Are Chinese drones spying on the U.S.?
While Chinese drones dominate the market, direct evidence linking them to spying incidents is limited. However, concerns about data transmission and potential espionage persist.
4. What are the penalties for illegal drone use?
Violations of FAA regulations can result in fines ranging from $1,000 to $25,000, depending on the severity of the incident.
5. What is the U.S. government doing about drone threats?
The U.S. has developed advanced counter-drone technologies and is working on stricter regulations for drone identification and operation.
6. Can drones be weaponized?
Yes. Drones can be modified to carry explosives, weapons, or chemical agents, though such cases are rare.
7. How common are drone incidents?
The FAA reported over 2,500 drone-related safety incidents in 2023, with many occurring near airports or restricted airspace.
8. What industries use drones in the U.S.?
Drones are widely used in industries like agriculture, construction, film production, and delivery services.
9. Are there international treaties on drone use?
Currently, no comprehensive international treaty governs drone use, though some bilateral agreements address specific issues.
10. How can individuals report suspicious drones?
Citizens can report suspicious drone activity to the FAA or local law enforcement through designated hotlines or online portals.
| The rise of mysterious drones in U.S. airspace highlights significant vulnerabilities in national security, legal frameworks, and public awareness. While some incidents may be benign, the potential for espionage and misuse underscores the urgent need for action. By enhancing regulations, deploying counter-drone measures, and addressing foreign-made technology risks, the U.S. can better protect its airspace and critical infrastructure. As the drone landscape evolves, vigilance and proactive policies will be key to maintaining safety and sovereignty. |