Inside RAF Fairford and Diego Garcia: Why the UK Blocked US Iran Strikes, Location, And History
 |
| UK refusing to allow Trump to use RAF bases to attack Iran |
In a rare diplomatic rupture between London and Washington, the United Kingdom has denied permission for the United States to use two key air force bases - RAF Fairford in England and the military base on Diego Garcia in the Indian Ocean - for potential strikes against Iran.
This decision has heightened tensions with U.S. officials, prompting sharp criticism and political pushback at the highest levels.
Read more: Where Are NATO Military Bases Located in Europe?
Which Bases the UK Refused and Why
RAF Fairford, Gloucestershire, England
 |
| RAF Fairford |
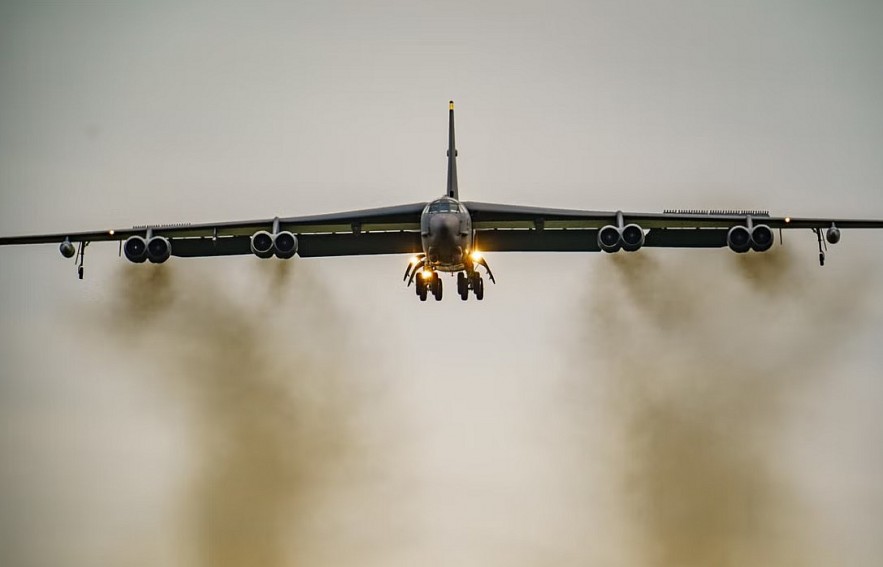
RAF Fairford is a Royal Air Force station located near Fairford in Gloucestershire, England. Originally built during World War II to support Allied operations in Europe, it later became one of the United States Air Force’s forward operating locations in Europe.
Under agreements between the UK and U.S., Fairford hosts U.S. bombers such as the B-1, B-2 and B-52 for exercises, forward deterrence deployments and training missions. It is the only European base routinely used by U.S. strategic bombers, giving Washington a physical location within striking distance of the Middle East.
Despite this long-standing military cooperation, the UK government has made it clear that UK clearance is required for offensive operations launched from the base. In the context of possible U.S. action against Iran, London has withheld this approval — partly due to concerns about violating international law and entangling Britain in a unilateral military campaign.
Read more: Where are US Military Deployments in the World and How Many Bases Are There
Diego Garcia – Indian Ocean Strategic Base
 |
| Diego Garcia, a British naval base |
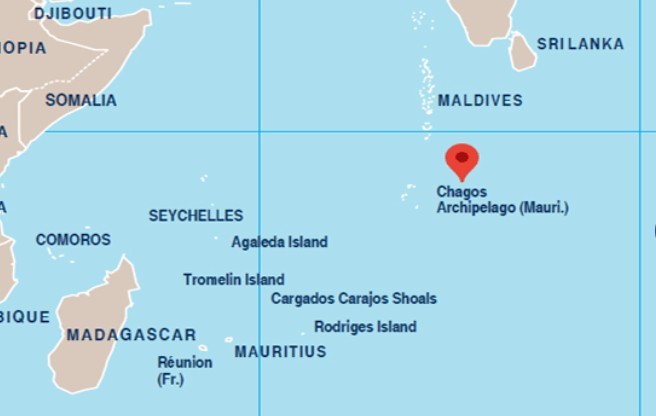
The second base the UK has blocked access to is located on Diego Garcia, the largest island of the Chagos Archipelago in the central Indian Ocean.
Although the territory is officially a British overseas territory, the island has hosted a joint UK-U.S. military facility since the 1970s, known as the Naval Support Facility Diego Garcia. The base has played a long-term strategic role for U.S. operations across the Middle East, South Asia and beyond, serving as a staging area for logistics, bombers, naval ships and refueling operations. It lies about 2,300 miles from Iran’s eastern border, making it a key fulcrum for long-range missions.
Under recent agreements, the UK has agreed to transfer sovereignty of the Chagos Islands to Mauritius while retaining a 99-year leaseback arrangement to keep the base operational. Even so, London has insisted that any use of Diego Garcia for offensive strikes must be explicitly approved by the UK government — approval that has not been granted in the current crisis.
Read more: Top 10 Largest U.S Military Bases In the World - Total 750 Bases (2023/2024)
History and Strategic Importance
RAF Fairford: From WWII to Strategic Bombers
RAF Fairford dates back to 1943 when it supported Allied aerial operations in World War II. After the war, it became a key site for U.S. Strategic Air Command missions during the Cold War, and later for NATO integrations and Bomber Task Force deployments.
Today, the base routinely supports U.S. forward bomber operations, reconnaissance missions and joint exercises with NATO allies, and its runway is capable of handling heavy bombers and large military aircraft. Its strategic presence in western Europe enhances deterrence and provides flexible power projection in regional crises.
 |
| Starmer blocks Trump from using RAF bases to strike Iran |
Diego Garcia: Vital Indian Ocean Pivot
Diego Garcia’s remote location makes it one of the most strategically advantageous military bases for operations across Africa, the Middle East and South Asia. Since the early 1970s, the U.S. Navy and later U.S. Air Force have used this base to support logistic prepositioning ships, strategic bombers, refueling tankers and naval vessels.
In conflicts from the Gulf War to Afghanistan and the fight against extremist groups, Diego Garcia has served as an important command and staging location. Its geographic position — far from congested airspace and near multiple theaters of operation — gives U.S. forces rapid access across vast regions.
Implications of the UK Decision
The refusal to grant U.S. forces access for potential strikes on Iran has political and military ramifications:
It reflects London’s concern about international law and political liability.
It underscores the UK’s control over military operations launched from its soil or territories covered by bilateral agreements.
It has prompted public criticism from U.S. officials and may influence broader diplomatic negotiations.
Whether these bases will remain central to future U.S. strategy in the region if the current standoff escalates remains a key question for analysts.
FAQs
Q: Why did the UK refuse to allow the U.S. to use these bases for strikes on Iran?
A: The UK government cited concerns over international law implications and not wanting to be legally implicated in offensive military operations without clear multilateral support.
Q: What is the strategic value of RAF Fairford?
A: It is the U.S. Air Force’s only forward bomber operating location in Europe, enabling long-range deployment and rehearsal of strategic bomber missions.
Q: Where is Diego Garcia, and why is it important?
A: Diego Garcia is a remote island in the Indian Ocean whose joint UK-U.S. base provides logistics, naval staging and bomber support across three continents.