U.S. Supreme Court is Likely to Force TikTok to Sell or Shut Down
 What is TikTok Account of School Shooter Natalie Rupnow What is TikTok Account of School Shooter Natalie Rupnow |
 Trump Asks Supreme Court to Pause TikTok Ban Trump Asks Supreme Court to Pause TikTok Ban |
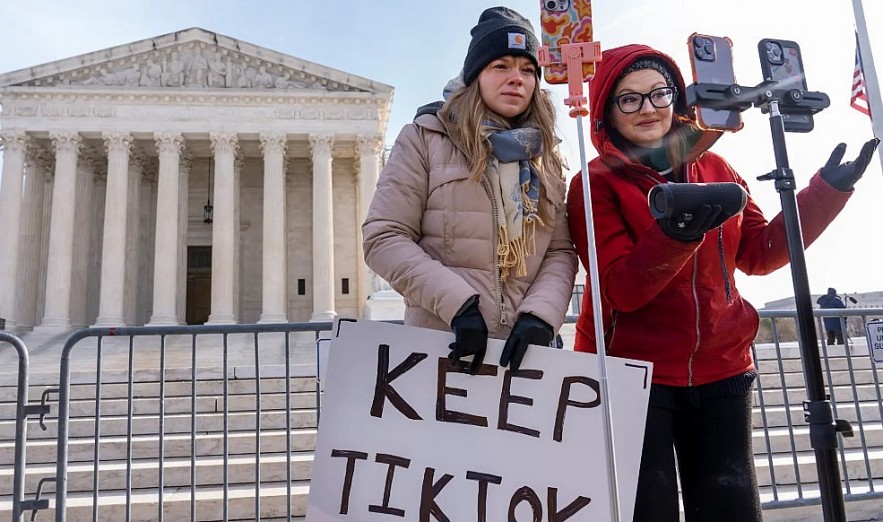 |
| Supreme Court seems likely to uphold a federal law that could force TikTok to shut down on Jan. 19 |
As tensions rise between the United States and China, the U.S. Supreme Court appears inclined to uphold a controversial law requiring TikTok’s Chinese parent company, ByteDance, to divest its ownership of the app or face a nationwide ban. The case, centered on national security concerns, highlights the broader geopolitical rivalry between the two countries and raises questions about data privacy, free expression, and global digital markets.
The Legal Foundation
The Protecting Americans from Foreign Adversary Controlled Applications Act (PAFACA), signed into law by President Joe Biden in 2024, aims to mitigate risks posed by foreign-owned applications that collect vast amounts of data from American users. The law specifically targets apps owned by entities in countries classified as “foreign adversaries,” which include China, North Korea, Russia, and Iran. TikTok, owned by Beijing-based ByteDance, has been the primary focus of this legislation due to its massive user base of approximately 170 million Americans.
Under the law, ByteDance is required to sell TikTok to a U.S. entity by January 19, 2025. Failure to comply would result in the app being banned from U.S. app stores and hosting platforms, effectively making it inaccessible to American users.
Supreme Court Hearings
On January 10, 2025, the Supreme Court heard oral arguments in the case of TikTok v. Garland. The questioning from the justices suggested a strong likelihood of upholding the law.
-
Chief Justice John Roberts emphasized the potential risks of ByteDance’s compliance with Chinese intelligence laws, which could force the company to share user data with the Chinese government. He noted the difficulty of ensuring data collected by TikTok would not be exploited for espionage or influence operations.
-
Justice Brett Kavanaugh pointed out that the issue was not about the content on TikTok but the ownership of the platform. He expressed concerns about the possibility of the Chinese government using the platform to manipulate public opinion or gather sensitive information.
-
Justice Samuel Alito dismissed claims that consumer warnings about TikTok’s potential misuse would suffice, stating that the legislation was designed to prevent hostile governments from accessing data on American citizens in the first place.
TikTok’s Defense
TikTok, represented by attorney Noel Francisco, argued that the law violates the First Amendment by targeting a platform that facilitates free expression. Francisco contended that the app’s content is protected speech and that banning TikTok or forcing a sale is an overreach based on speculative future threats.
Francisco also highlighted the logistical and technical challenges of separating TikTok’s operations from ByteDance within such a short timeframe. TikTok has expressed doubts about its ability to find a U.S. buyer and complete the sale by the deadline.
National Security Concerns
Central to the case are fears about how data collected by TikTok might be misused. The app gathers extensive information from its users, including:
- Personal and demographic data
- Location tracking
- Behavioral patterns
- Search and browsing history
Critics argue that this data could be accessed by the Chinese government to conduct espionage, influence campaigns, or even blackmail individuals. The U.S. government’s position reflects a broader distrust of Chinese technology companies and their potential ties to the Chinese Communist Party.
Out of the 193 United Nations member states, only four—China, North Korea, Russia, and Iran—are classified as foreign adversaries under U.S. law. The legislation aims to ensure that companies from these countries do not gain control over platforms that could compromise American security.
Political and Historical ContextThe controversy over TikTok’s ownership is not new. In 2020, then-President Donald Trump attempted to ban TikTok through an executive order, citing national security risks. However, courts blocked the move, ruling that such actions required congressional approval. This led to the creation of PAFACA, which passed with bipartisan support in both chambers of Congress. The current administration has taken a firm stance on the issue. President Biden, while facing criticism from TikTok users and free speech advocates, has defended the law as a necessary measure to protect national security. |
Broader Implications
The Supreme Court’s decision will have far-reaching consequences:
-
Impact on TikTok: If the law is upheld, ByteDance must sell TikTok to a U.S.-based entity or face a ban. This could set a precedent for other foreign-owned apps operating in the U.S.
-
Data Privacy Standards: The case underscores the growing importance of data privacy in national security debates. It could prompt further scrutiny of foreign-owned tech companies.
-
Geopolitical Dynamics: The case highlights the ongoing rivalry between the U.S. and China in the digital and technological spheres. A forced sale or ban could escalate tensions between the two nations.
-
Consumer Access and Expression: For TikTok users, the potential ban raises concerns about access to a platform that has become a major medium for entertainment, education, and self-expression.
What’s Next?
As the January 19 deadline approaches, ByteDance faces immense pressure to find a U.S. buyer. Analysts have speculated that major tech companies, such as Microsoft or Oracle, might express interest in acquiring TikTok. However, the short timeline and the app’s complex operational structure pose significant challenges.
If ByteDance fails to divest, the app could be removed from U.S. app stores and web hosting services, effectively cutting off American users. This would mark the most significant restriction of a social media platform in the country’s history.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court’s forthcoming ruling will shape the future of TikTok in the United States and set a critical precedent for how governments address national security concerns in the digital age. While the platform’s supporters argue for its cultural and social value, policymakers remain focused on mitigating risks associated with foreign ownership. Whether through a sale or a ban, the outcome will mark a defining moment in the intersection of technology, security, and global politics.
 Top 10 Most Popular U.S. Artists on TikTok Top 10 Most Popular U.S. Artists on TikTok 2024 has been an incredible year for TikTok and its top US artists, with over 279 million combined followers. From viral dances to global tours, ... |
 TikTok Ban in the US: What’s happening, Why it matters, and What comes next TikTok Ban in the US: What’s happening, Why it matters, and What comes next The potential ban on TikTok in the United States has sparked a heated debate, touching on national security, tech rivalry, and freedom of expression. |
 Who is Olivia Ponton: TikTok star, LGBTQ+ Representation, and Net Worth Who is Olivia Ponton: TikTok star, LGBTQ+ Representation, and Net Worth Now a social media celebrity, Olivia Ponton has a staggering 2.9 million followers on Instagram and 7.6 million on TikTok. She has also become a ... |
 TikTok faces potential ban in the U.S if not sold by January 2025: Waiting for President Donald Trump TikTok faces potential ban in the U.S if not sold by January 2025: Waiting for President Donald Trump The Supreme Court on Wednesday agreed to hear arguments by TikTok that a law that could lead to a ban of the popular social media ... |