Who Are the Syrian Rebels in Aleppo: Key Leaders, Fighters, and Supporters
Syrian Rebels Sweep into Aleppo
Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) has intensified its operations, pushing further into Aleppo after years of consolidating power in Syria's northwest. Recent reports indicate that HTS is seizing strategic territories previously held by rival rebel factions and the Syrian government. These advances come amidst increasing clashes, signaling a potential shift in the Syrian conflict's dynamics.
Key strategic gains include controlling vital supply routes and checkpoints around Aleppo. This territorial expansion underscores their operational sophistication, with well-coordinated military strategies and superior combat readiness. Observers note that HTS is leveraging weakened opposition forces and exploiting divisions among rival groups to consolidate its dominance.
However, HTS's expansion raises alarms internationally due to their hardline Islamist ideology and reported links to al-Qaeda, despite officially severing ties. The Syrian government, supported by Russia and Iran, has ramped up airstrikes targeting HTS positions, intensifying hostilities in the region.
Civilians remain the primary victims of this escalation, facing displacement, shortages of essential supplies, and heightened insecurity. International humanitarian organizations are calling for urgent aid to address the worsening crisis. Meanwhile, Western nations remain cautious about intervention, given the complexities of Syria's multifaceted conflict.
HTS's advance into Aleppo marks a critical juncture in Syria's prolonged war, posing challenges to regional stability and complicating the prospects for peace negotiations.
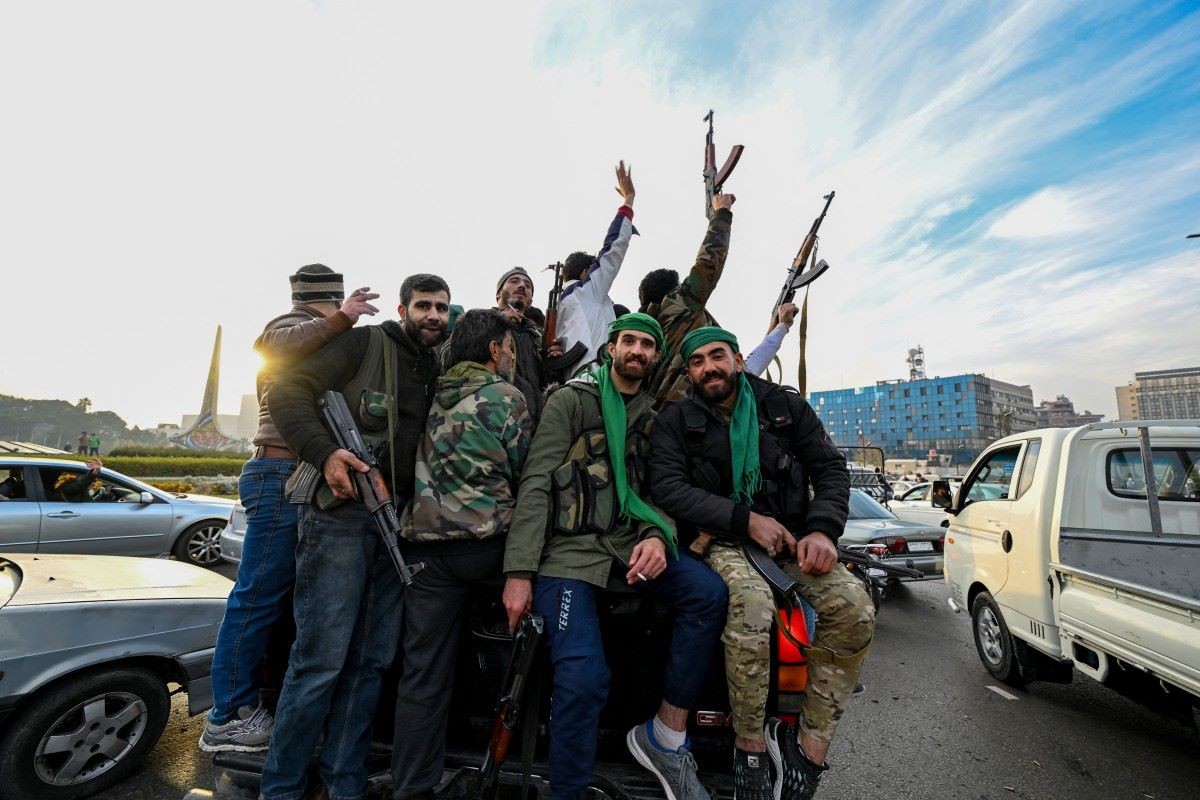
 |
| Anti-government fighters brandish their guns as they ride a vehicle in Syria's northern city of Aleppo |
How Strong is Hayat Tahrir al-Sham?
Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) has established itself as one of the most formidable rebel forces in Syria. Its strength can be assessed through several factors:
Membership
HTS is estimated to have between 12,000 and 20,000 fighters, including seasoned veterans from Syria and abroad. This diverse composition includes former members of other Islamist groups and foreign jihadists. Their fighters are well-trained in guerrilla tactics and equipped with modern weaponry.
Military Arsenal
HTS possesses a wide array of weapons, including:
- Armored vehicles and tanks captured from battles.
- Advanced drones used for reconnaissance and attacks.
- Anti-aircraft and anti-tank missiles, many obtained from the black market or battlefield gains.
Their ability to mobilize forces quickly and execute coordinated attacks gives them a tactical advantage over rival factions and the Syrian regime.
Territorial Control and Revenue
HTS dominates large parts of Idlib province and has begun expanding into Aleppo. These territories provide access to critical infrastructure, including roads and border crossings. HTS generates substantial revenue from:
- Taxes and tariffs on goods passing through checkpoints.
- Fees levied on businesses and residents in areas under their control.
- Alleged donations from private individuals sympathetic to their cause.
The group's financial and logistical resources have allowed them to maintain a robust military and administrative presence despite external challenges.
History and Development of Hayat Tahrir al-Sham
Origins
HTS was officially formed in January 2017 as a coalition of several Islamist factions. The most prominent group in this merger was Jabhat Fateh al-Sham, previously known as the Nusra Front, which had been al-Qaeda’s affiliate in Syria.
HTS was established with the goal of uniting Islamist factions under a single umbrella. By officially severing ties with al-Qaeda, the group sought to rebrand itself and gain broader legitimacy among Syria’s opposition forces.
Development and Strategy
Since its inception, HTS has evolved significantly:
- Tactical Pragmatism: HTS has adapted its strategies to maintain control. For instance, while adhering to its Islamist ideology, it has engaged in localized governance to secure the loyalty of populations in areas it controls.
- Administrative Governance: HTS established the "Salvation Government" in Idlib, which oversees services such as healthcare, education, and law enforcement. This quasi-governmental structure has helped the group project an image of authority and stability.
- Rivalry and Consolidation: HTS has aggressively eliminated rival factions, either by absorbing them or neutralizing them through military force. This has enabled the group to consolidate its position as the dominant force in northwest Syria.
Despite its rebranding efforts, HTS continues to face accusations of authoritarian rule, including suppressing dissent and targeting moderate opposition figures.
Who Supports Hayat Tahrir al-Sham?
The rise of HTS has been fueled by a complex web of local and international support:
Private Donors
Wealthy individuals from the Gulf States have historically supported Islamist groups in Syria, including HTS. These donors provide financial aid, often under the guise of humanitarian assistance.
Turkey’s Role
Turkey’s relationship with HTS is complicated. While Turkey officially denies supporting HTS, it has strategic interests in maintaining influence in northern Syria to counter the Kurdish presence and the Assad regime. Observers note that Turkey has tolerated HTS’s dominance in Idlib, given the group’s role in preventing Kurdish expansion.
Revenue from Controlled Areas
HTS generates significant income from the territories it governs. Taxes, customs duties, and the management of public resources contribute to its financial stability, enabling the group to sustain its military operations.
Leadership of Hayat Tahrir al-Sham
HTS is led by Abu Mohammed al-Jolani, a controversial and enigmatic figure. His leadership has been pivotal in shaping HTS’s strategy and maintaining its relevance in Syria's volatile conflict.
Abu Mohammed al-Jolani
- Background: Jolani was initially an operative in al-Qaeda in Iraq, where he worked closely with Abu Musab al-Zarqawi. He later returned to Syria during the Civil War, founding the Nusra Front.
- Leadership Style: Jolani combines ideological commitment with pragmatic flexibility, enabling HTS to adapt to changing circumstances. His decision to sever ties with al-Qaeda was a strategic move to broaden the group’s appeal.
Other Key Leaders
- Abu al-Fatah al-Farghali: A senior military strategist responsible for coordinating large-scale offensives.
- Abu Malek al-Talli: Oversees recruitment, propaganda, and public relations.
HTS’s leadership team reflects a mix of ideological rigidity and strategic adaptability, ensuring the group’s continued dominance.
What Major Powers Are at Play in the Syrian Conflict?The Syrian conflict remains a stage for competing international interests, with major powers backing different sides while carefully managing their involvement to avoid escalation. Here's a breakdown of their roles and actions: Russia and Iran: Supporting the Assad RegimeRussia: The Kremlin reiterated its hope that the Syrian government would swiftly “restore order” in Aleppo following the recent offensive by Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS). Russia has been a staunch ally of Bashar al-Assad, providing military support, airpower, and diplomatic backing since entering the conflict in 2015. Moscow’s involvement has been pivotal in helping Assad reclaim lost territories and suppress opposition forces. Iran: Tehran views Syria as a critical ally in its regional strategy and has blamed the Aleppo offensive on an “American-Israeli plot” aimed at destabilizing the region. Iran provides ground support through its Revolutionary Guard and affiliated militias, including Hezbollah, solidifying its influence in the Syrian theater. Turkey: A Balancing ActTurkey remains a key player, with its forces and allied rebel factions controlling significant portions of northern Syria. Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan initially sought to overthrow Assad when the conflict erupted in 2011. However, as Assad regained control over much of Syria, Turkey shifted its strategy, focusing on curbing Kurdish influence near its borders and maintaining leverage over rebel groups. Current Role: Turkey has demanded an end to attacks on Idlib, a rebel stronghold where Syrian and Russian airstrikes have intensified. Ankara’s reaction to the latest offensive will be critical. Analysts suggest that if rebel gains persist, Turkey might escalate its involvement, potentially heightening tensions with Damascus and its backers. Western Powers: Limited EngagementThe United States and its allies have largely stepped back from direct involvement in Syria’s shifting power dynamics, focusing instead on counterterrorism operations, particularly against ISIS. Their absence has created a vacuum that regional powers like Russia, Iran, and Turkey have filled. Stalled Rapprochement Between Turkey and SyriaEfforts to normalize relations between Turkey and the Assad regime, encouraged by Moscow and Tehran, have stalled. Despite talks of détente, mistrust and conflicting interests continue to prevent a breakthrough. For Turkey, securing its borders and ensuring influence in northern Syria remain top priorities, while Assad seeks to reassert control over the entire country. The evolving power struggle in Syria reflects broader geopolitical rivalries. The Aleppo offensive and its aftermath could redefine alliances and influence, testing the limits of each major power’s commitment and shaping the next phase of the conflict. |
Analysis and Observations
Hayat Tahrir al-Sham has demonstrated remarkable resilience and adaptability in Syria’s conflict. Its evolution from an al-Qaeda affiliate to a quasi-governmental force underscores its ability to navigate complex political and military landscapes.
However, HTS’s hardline ideology and authoritarian practices alienate potential allies, limiting its broader appeal. Furthermore, its designation as a terrorist organization by many nations hinders its participation in peace negotiations and restricts international engagement.
The group’s growing influence poses significant challenges:
- For the Assad regime: HTS remains one of the most formidable opponents, undermining government efforts to reclaim lost territory.
- For international actors: HTS complicates efforts to achieve a peaceful resolution in Syria, as its extremist roots make it a contentious player in any negotiations.
Conclusion
Hayat Tahrir al-Sham is a dominant yet polarizing force in Syria's ongoing war. Its military strength, territorial control, and governance structures make it a significant actor in the conflict. However, its extremist ideology and controversial tactics pose challenges to both its long-term viability and the broader pursuit of peace in Syria.
As the situation in Aleppo and beyond evolves, understanding HTS’s motivations, strategies, and impact is critical to addressing the complexities of the Syrian Civil War.
FAQs
1. What are HTS's ultimate goals?
HTS aims to establish an Islamist state governed by strict sharia law, particularly in areas under its control.
2. Is HTS linked to al-Qaeda?
While HTS originated as an al-Qaeda affiliate, it officially severed ties to rebrand and attract broader support.
3. How does HTS fund its operations?
The group generates revenue from taxes, customs duties, and private donations, as well as battlefield acquisitions.
4. What challenges does HTS face?
HTS faces opposition from rival factions, targeted airstrikes from the Syrian regime and Russia, and international condemnation.
5. Can HTS participate in peace talks?
HTS’s inclusion in peace talks remains unlikely due to its designation as a terrorist organization and its hardline Islamist stance.
 Syrian National Anthem: English Translation, Original Lyrics And History Syrian National Anthem: English Translation, Original Lyrics And History "Ḥumāt ad-Diyār" is the national anthem of the Syrian Arab Republic, with lyrics written by Khalil Mardam Bey and the music by Mohammed Flayfel. If ... |