Australia Becomes the First Country to Ban Social Media for Children Under 16
 Age Restrictions on Social Media: Insights from Australia's Proposal Age Restrictions on Social Media: Insights from Australia's Proposal In a groundbreaking move, Australia is considering a nationwide ban on social media usage for individuals under 16 years old. |
 |
| Australia passes social media ban for children under 16 |
This unprecedented legislation, passed by the Australian Parliament, is a groundbreaking step in addressing the increasingly significant issues surrounding social media usage among minors. The decision has sparked a global conversation about the role of social media in society, its impact on young people, and the responsibilities of governments in regulating technology.
This legislation establishes one of the strictest regulatory frameworks targeting Big Tech, potentially setting a global precedent.
The law mandates tech giants such as Meta, the parent company of Instagram and Facebook, as well as TikTok, to prevent minors from accessing their platforms. Non-compliance could result in fines of up to A$49.5 million (approximately $32 million). A pilot program to test enforcement measures will begin in January, with the full ban slated to take effect within a year. The Social Media Minimum Age Bill positions Australia as a global test case for governments increasingly seeking to legislate age restrictions on social media, driven by concerns over its impact on young people’s mental health.
| Unlike other jurisdictions, such as France and certain U.S. states, where laws require parental consent for minors to access social media, Australia’s ban is unequivocal. Meanwhile, a similar proposal in Florida, which includes a full ban for users under 14, is currently facing legal challenges over free speech rights. |
The Background and Purpose of the Law
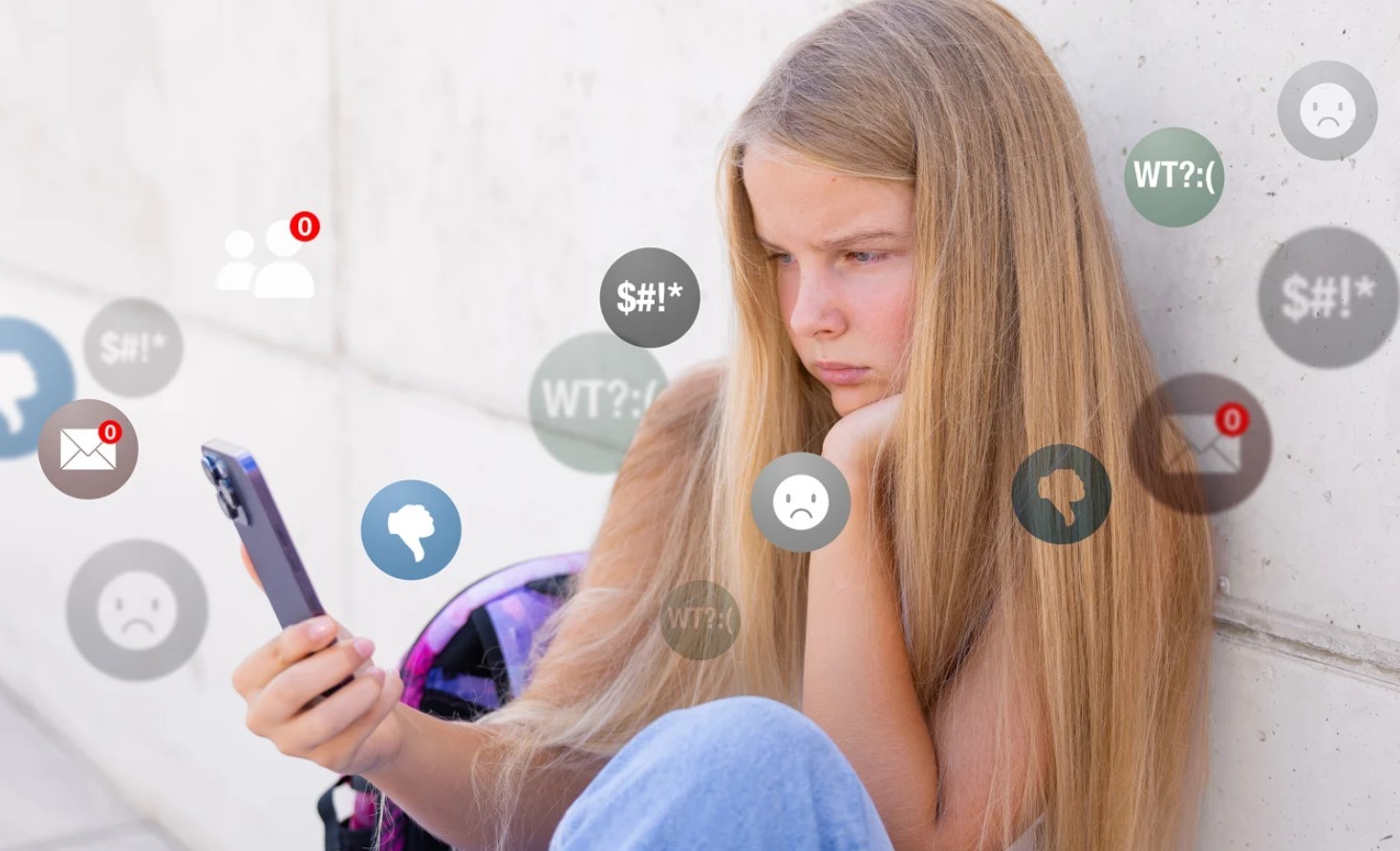
The newly introduced legislation comes in response to growing concerns over the negative effects of social media on young users. Studies from around the globe have highlighted the detrimental impact of social media on mental health, self-esteem, and social development. Cyberbullying, exposure to inappropriate content, and addictive behaviors are just a few of the challenges faced by minors navigating online spaces.
The Australian government justified the ban by pointing to these risks and arguing that children under 16 lack the maturity to use such platforms responsibly. The law also aims to protect younger users from the exploitation of personal data by social media companies, which often monetize user interactions without adequate safeguards for minors.
The law mandates strict age verification processes on all social media platforms operating in Australia. Companies failing to comply with these regulations face substantial fines and could even be banned from the Australian market.
The Arguments For the Ban
Supporters of the legislation argue that it is a necessary intervention in a time when social media is increasingly pervasive in daily life. Key arguments include:
Mental Health Protection:
Research has consistently shown that excessive social media use among teenagers correlates with higher rates of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. Platforms like Instagram and TikTok, which often emphasize curated lifestyles and appearance-focused content, have been linked to body image issues and unhealthy comparisons. By preventing younger users from accessing these platforms, the law aims to create a safer developmental environment.
Shielding from Cyberbullying:
Cyberbullying is a pervasive problem on social media, disproportionately affecting younger users. A ban could significantly reduce exposure to harmful interactions and the psychological damage they cause.
Data Privacy Concerns:
Many social media platforms collect vast amounts of data from their users, including minors. Critics argue that children are often unaware of how their data is used or shared, making them vulnerable to exploitation. The ban prevents minors from inadvertently compromising their privacy.
Encouraging Offline Interactions:
The legislation encourages children to engage in real-life social interactions and activities rather than spending excessive time in virtual spaces. Advocates believe this shift could foster healthier relationships and hobbies, contributing to better emotional and physical well-being.
Criticism and Challenges
Despite its noble intentions, the law has faced significant criticism from various quarters. Opponents of the legislation have raised several concerns, including:
Freedom of Expression:
Critics argue that the ban infringes on the fundamental rights of young people to express themselves and participate in online communities. Social media platforms often serve as avenues for creative expression, education, and activism, and the prohibition could limit these opportunities.
Practicality of Enforcement:
Implementing the law presents significant challenges. Age verification processes, while mandatory under the new legislation, are not foolproof. Children could easily find ways to bypass these restrictions using false information or accounts set up by older individuals.
Impact on Marginalized Groups:
For some young people, especially those from marginalized communities, social media provides a critical platform for finding support, resources, and like-minded individuals. A blanket ban could isolate these individuals from vital online networks.
Parental Autonomy:
Many argue that decisions about social media usage should be left to parents, not the government. Critics fear that the law undermines parental authority and places too much control in the hands of the state.
Global Implications
Australia’s decision to implement such a stringent measure has sparked a global debate. Governments, social media companies, and child advocacy groups worldwide are watching closely to see the law's outcomes.
Some countries, particularly those with high rates of youth social media addiction, may consider adopting similar measures. However, others may view the ban as overly restrictive, favoring education and digital literacy programs instead of outright prohibition.
Social media companies will also be affected on a global scale. If the law proves successful, it could push platforms to rethink their policies, particularly regarding age restrictions and content moderation.
The Role of Social Media Companies
The legislation places significant responsibility on social media companies to ensure compliance. These companies must now implement rigorous age verification systems, which could involve new technologies like biometric scans, government ID verification, or parental consent mechanisms.
However, the law also opens up debates about the ethical responsibilities of these companies. Critics argue that social media platforms have long prioritized profit over the well-being of users, particularly minors. This legislation could mark a turning point, forcing companies to adopt more ethical practices.
Alternative Approaches to the Problem
While the Australian law is groundbreaking, it is not the only approach to addressing the challenges posed by social media for young users. Alternatives include:
Education and Digital Literacy:
Teaching young people how to navigate social media responsibly can empower them to make better choices without needing a total ban. Schools could introduce mandatory classes on digital etiquette, privacy, and the psychological effects of social media.
Stronger Content Moderation:
Platforms could be required to implement stricter moderation policies, ensuring that harmful content is removed and that minors are shielded from inappropriate material.
Time Limits and Usage Restrictions:
Instead of a complete ban, imposing daily time limits on social media use for minors could reduce the risks associated with excessive screen time.
Parental Control Tools:
Enhancing parental control features on social media platforms could allow parents to monitor and regulate their children’s online activities more effectively.
The Path Forward
The success of Australia’s law will depend largely on its enforcement and the cooperation of social media companies. In addition, the government must invest in complementary measures such as public awareness campaigns, support for mental health services, and ongoing research into the impact of social media on young people.
If successful, the legislation could serve as a model for other countries grappling with similar challenges. However, the law’s critics underscore the importance of balancing regulation with individual freedoms and practical enforcement strategies.
Conclusion
Australia’s decision to ban social media for individuals under 16 is a bold and controversial move that highlights the growing global concerns over the impact of technology on youth. While the law has the potential to mitigate some of the most pressing issues associated with social media use among minors, it also raises significant questions about enforcement, freedom of expression, and parental autonomy.
The world will be watching closely as Australia implements this legislation, which may well set a precedent for future policies around the globe. Whether the law ultimately succeeds or faces insurmountable challenges, it has undeniably ignited a critical conversation about the role of technology in shaping the lives of the next generation.
 Who is the Most Followed Person on Social Media (2024 Update) Who is the Most Followed Person on Social Media (2024 Update) The most popular accounts on social media, whether they are celebrities or brands, can reach a global audience of millions. |
 Using Bluesky: A Beginner's Guide to Decentralized Social Media Using Bluesky: A Beginner's Guide to Decentralized Social Media Bluesky is a decentralized social media platform that will change online communication. Based on AT Protocol, Bluesky prioritizes user control, interoperability, and privacy. Beginners can ... |
 Social Media Buzzes as Kai Trump Performs Donald Trump's YMCA Dance Social Media Buzzes as Kai Trump Performs Donald Trump's YMCA Dance In a recent social media post, Kai Trump, the 17-year-old granddaughter of President-elect Donald Trump, shared a TikTok video where she emulated her grandfather's well-known ... |
 Bluesky Under Scrutiny: EU Compliance Challenges for Emerging Social Media Platforms Bluesky Under Scrutiny: EU Compliance Challenges for Emerging Social Media Platforms The European Union says Bluesky violates the EU Digital Services Act rules around information disclosure. This article explores the details of the case, Bluesky's regulatory ... |