Border Patrol Agents Explained: Who They Are, What They Do, and How They Differ from ICE Agents
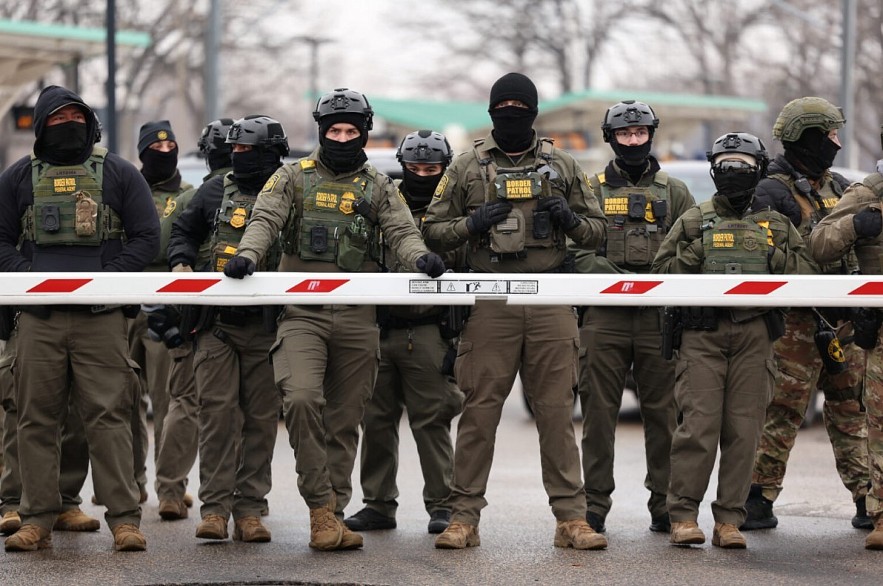 |
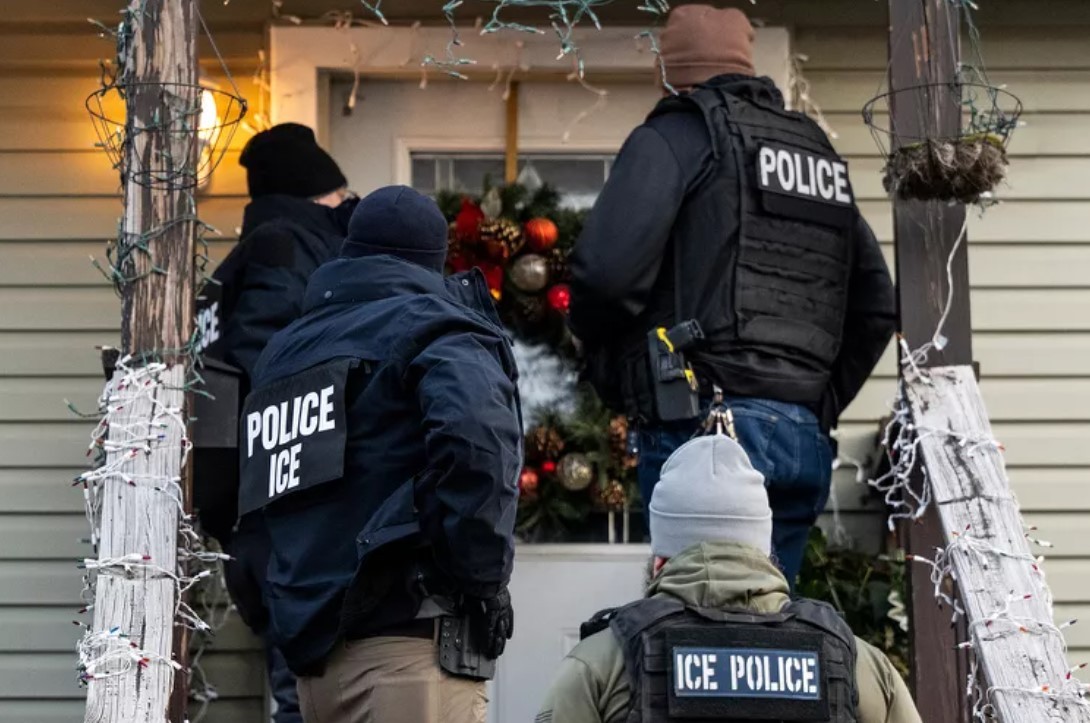
| US Border Patrol agents stand guard at the Bishop Henry Whipple Federal Building in Minneapolis, Minnesota |
In discussions about U.S. immigration enforcement — from border security to high-profile incidents such as the shooting of Alex Pretti — two terms often surface: Border Patrol agents and ICE agents.
Although both enforce immigration laws under the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), their missions, authorities, and day-to-day responsibilities are very different. Understanding these differences is key for anyone following debates on immigration, civil liberties, law enforcement authority, or national security.
Read more: ICE Agents Explained: Who They Are, What They Do, and Why They’re Under Scrutiny
Who Are Border Patrol Agents?
U.S. Border Patrol agents are federal law enforcement officers employed by U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), a large component of DHS tasked with protecting America’s borders. Border Patrol’s chief mission is to detect and prevent the unlawful entry of people and contraband into the United States, especially between official ports of entry along the U.S.–Mexico and U.S.–Canada borders.
Border Patrol agents operate in the field — on foot, in vehicles, on horseback, by air, and with surveillance technology — watching for signs of unauthorized entry, tracking cross-border movement, and intercepting people or goods attempting to enter without inspection.
Their work involves:
-
Monitoring remote border areas with sensors and cameras.
-
Apprehending individuals who attempt to cross illegally between ports of entry.
-
Conducting searches and seizures under immigration and customs law.
Border Patrol agents receive specialized training for field operations, tracking, and enforcement work, with a focus on border interdiction and surveillance rather than interior immigration policies.
What Are ICE Agents?
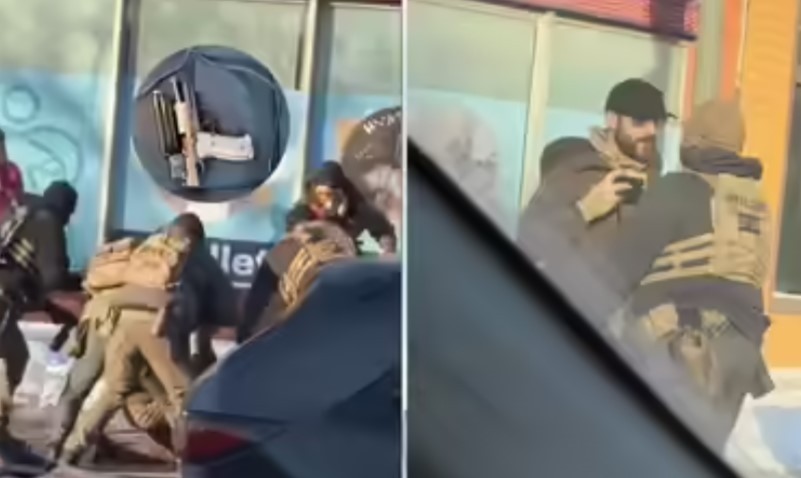
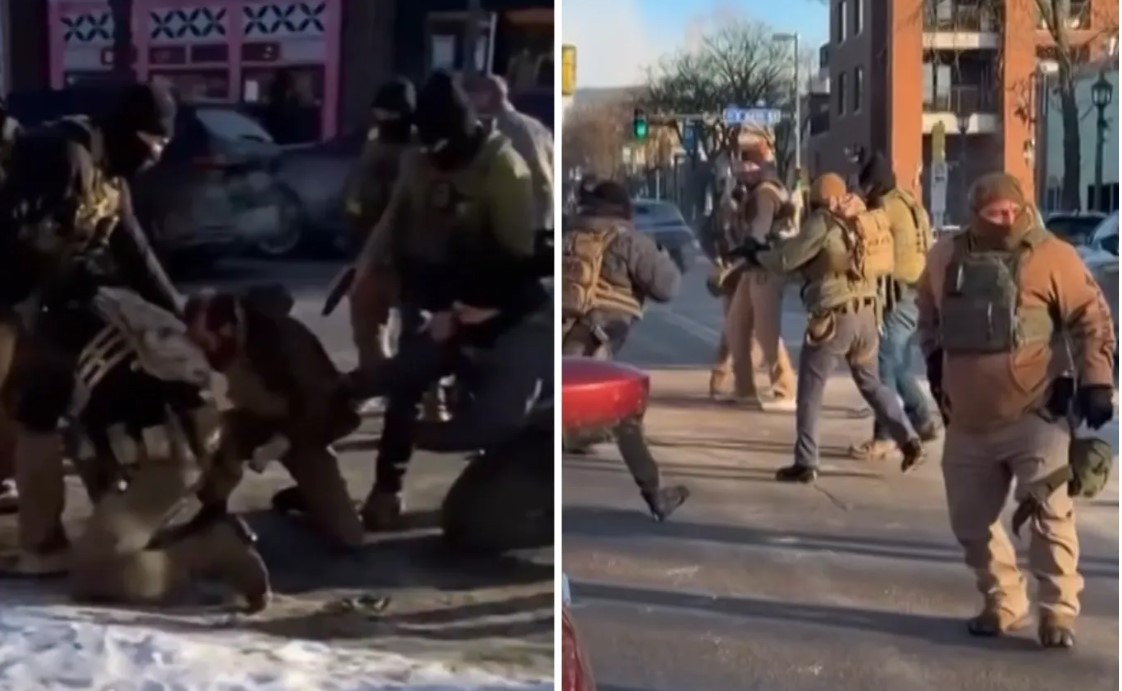
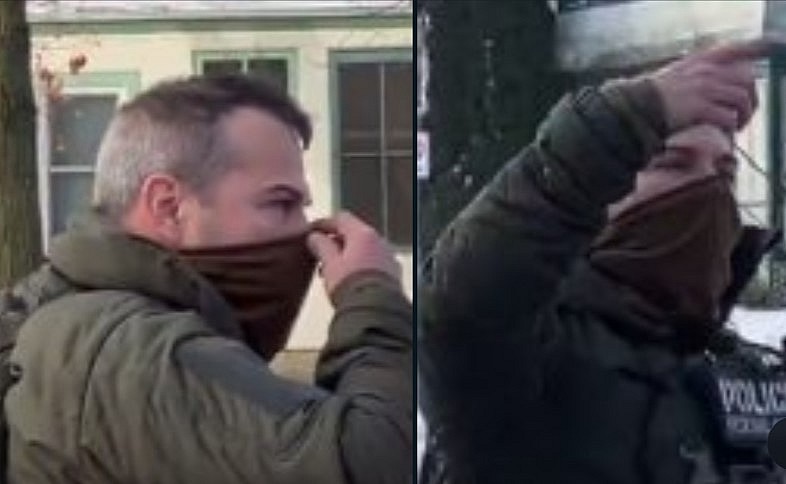 |
| The ICE agent believed to have fatally shot Renee Nicole Good in south Minneapolis, though authorities have not confirmed the agent’s identity or verified the images |
Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) is a separate DHS agency created after the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks to enforce immigration and customs laws both at and inside the homeland, focusing on areas away from the immediate border.
ICE has two major operational divisions:
-
Enforcement and Removal Operations (ERO) — ERO is responsible for identifying, arresting, detaining, and removing (deporting) non-citizens who violate immigration laws. These violations may include unlawful presence, criminal convictions, or immigration warrants.
-
Homeland Security Investigations (HSI) — HSI conducts criminal investigations into serious transnational crimes such as human trafficking, drug smuggling, financial fraud, and other activities that intersect with immigration and customs law.
Unlike Border Patrol agents, ICE agents generally:
-
Work within the interior of the United States, not primarily at the border.
-
Execute arrest and removal orders, not initial border interdiction.
-
Conduct criminal investigations alongside local, state, and international partners.
ICE agents may operate in workplaces, communities, transportation hubs, and detention centers. They often work on complex cases that involve collaboration with the Department of Justice and other federal agencies.
Read more:
- Can You Record ICE Agents? and What Your Rights Are After the Minneapolis Shooting
- Why Prosecuting the ICE Agent in the Renee Good Shooting Is Unlikely
Key Differences Between Border Patrol and ICE Agents
This difference means that while both enforce immigration law under DHS, their roles are distinct: Border Patrol works at the border’s edge, and ICE works inside the country’s interior and legal system.
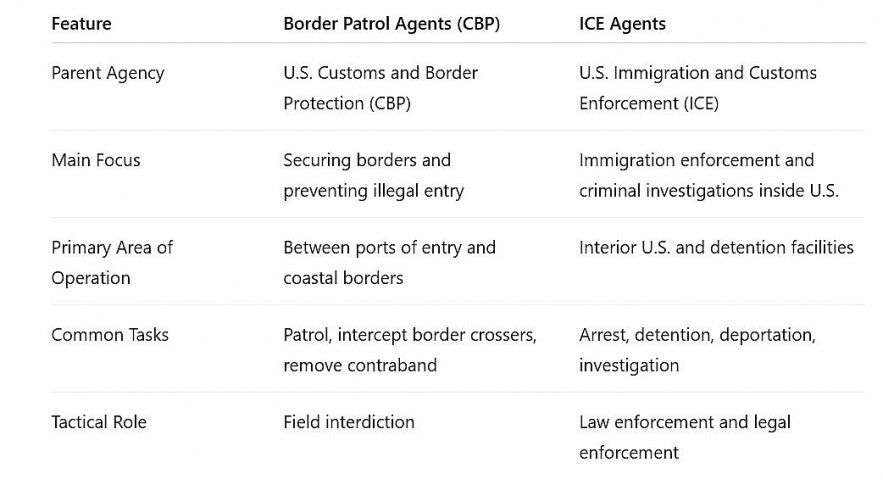 |
| Differences Between Border Patrol and ICE Agents |
How Their Authorities Overlap and Diverge
Both Border Patrol and ICE agents have the authority to arrest and detain individuals suspected of violating immigration laws. However, their jurisdiction, goals, and tactics differ:
-
Border Patrol authority extends to preventing entry and apprehending unauthorized arrivals before they reach the interior. Agents focus on real-time interdiction and surveillance, using field positions and sensors to detect activity.
-
ICE authority includes investigations, interior arrests, and removals. ERO agents may arrest individuals based on warrants or removal orders issued by immigration courts, while HSI handles complex criminal cases.
These differences also influence how each agency approaches enforcement actions, community interaction, and public perception.
Why the Distinction Matters in Public Debate
In incidents like the Minneapolis shooting of Alex Pretti, understanding the difference between Border Patrol agents and ICE agents helps clarify who was involved, why they were deployed, and what legal frameworks govern their actions.
Border Patrol agents, trained for border interdiction, have increasingly been deployed in city environments during immigration enforcement operations, sometimes sparking controversy because this is outside their traditional border mission.
ICE agents, on the other hand, are more accustomed to interior enforcement and investigative work, often working with federal, state, and local courts rather than field interdiction roles.
Conclusion
Border Patrol and ICE agents are both key components of the U.S. immigration enforcement system under the Department of Homeland Security, but their missions, authorities, and areas of operation differ significantly. Border Patrol agents focus on securing the border and preventing unauthorized entry, while ICE agents enforce immigration laws inside the United States and investigate related criminal activity. Understanding these differences helps make sense of current debates on immigration policy, federal policing, and public safety through the lens of real-world events.