Does Ukraine Have Nuclear Weapon?
Does Ukraine Have Nuclear Weapons Now?
There are no nuclear weapons in Ukraine's arsenal. In exchange for security guarantees, Ukraine signed the Budapest Memorandum in 1994 and relinquished its nuclear arsenal, which was the third-largest in the world at the time.
Following the removal of the last warhead from the country on June 2, 1996, Ukraine lost its nuclear status. Since then, the country has faithfully adhered to its non-nuclear-weapons-state obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty.
Learn more: Zaporizhzhia - Ukraine’s Largest Nuclear Plant with 6 Reactors
 |
| Nuclear complex SS-20 Saber in Vinnytsia, Ukraine |
Does Ukraine Really Want Nuclear Weapon?
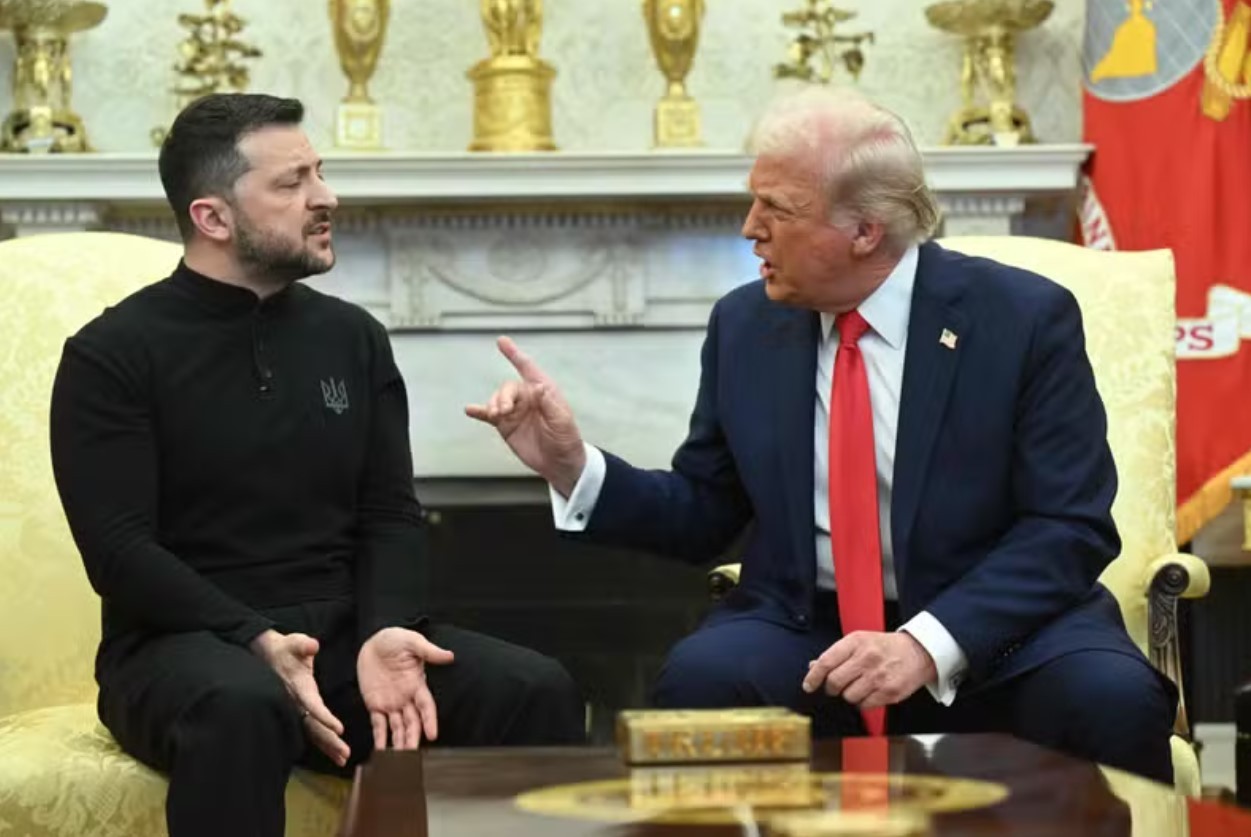
Earlier this week, during a discussion on the necessary measures to safeguard the eastern European nation still fighting off Moscow's invasion, Volodymyr Zelenskyy informed the European Council that, barring NATO membership, the sole choice for Ukraine would be nuclear weapons.
Did Ukraine have nuclear weapons?
Yes, in 1991, Ukraine regained independence and inherited the nuclear weapons from the USSR that were located and produced on Ukrainian territory. Before signing the Budapest Memorandum, Ukraine was the third nuclear power in the world.
Kyiv has reiterated its commitment to nuclear non-proliferation and has stated that it has no plans to develop WMD in a statement released by the Ukrainian foreign ministry.
After that, Zelenskyy had to elaborate on how he was showing how bad things were for Kyiv by bringing up the 1994 Budapest Memorandum, wherein the three major nuclear powers—Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States—exchanged security assurances for Ukraine's nuclear arsenal.
How Many Nuclear Weapons Did Ukraine Have?
After the collapse of the USSR, Ukraine inherited 176 intercontinental ballistic missiles in launch silos and more than 4,000 nuclear warheads. Ukraine also had 103 strategic bombers of various modifications.
At the time, Ukraine had about a third of the Soviet Union's nuclear arsenal, which was the third largest in the world. It also had a lot of the tools used to make and design nuclear weapons.There were still 130 UR-100N/RS-18 intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) with six warheads each, 46 RT-23 Molodets ICBMs with ten warheads each, and 33 heavy bombers in Ukraine, for a total of about 1,700 warheads.
Forty underground launch silos for RT-23 ICBMs had been set up around the city of Pervomaisk in the Mykolaiv Oblast. This is where the 46th Rocket Division of the 43rd Rocket Army of the Soviet Strategic Rocket Forces is based. The individual silos were spread out across the area. They were often set up in fields and surrounded by fences with guards watching over them. A group of nine or ten silos were linked to an underground Unified Command Post that was staffed by several military officers.
Ukraine was home to the following nuclear force units when it was a republic in the Soviet Union:
43rd Rocket Army
19th Rocket Division (Rakovo, Khmelnytskyi Oblast) (see uk:19-та ракетна дивізія (СРСР))
37th Guards Rocket Division (Lutsk, Volyn Oblast)
43rd Guards Rocket Division (Romny, Sumy Oblast)
46th Rocket Division (Pervomaisk, Nikolayev Oblast)
50th Rocket Division (Bilokorovychi, Zhitomir Oblast)
 |
| SS-18 Satan nuclear missile fully designed and manufactured in Ukraine at Yuzhmash |
Why did Ukraine Give up Nuclear Weapons?
An important question concerning the nuclear arsenal that Ukraine possessed emerged when it gained independence. Most concerning to Russia and the United States were Ukraine's nuclear capabilities. These nations made disarming Ukraine their top priority in the early 90s. Once the Soviet Union fell, new nations emerged on the global stage and vied for a position in the post-Soviet global order. These were uncertain times of transition.
Upon Ukraine's declaration of independence, Russia wasted no time in making territorial claims and threats against the country.
Then, faced with a choice, Ukraine opted for nuclear disarmament in return for international security guarantees.
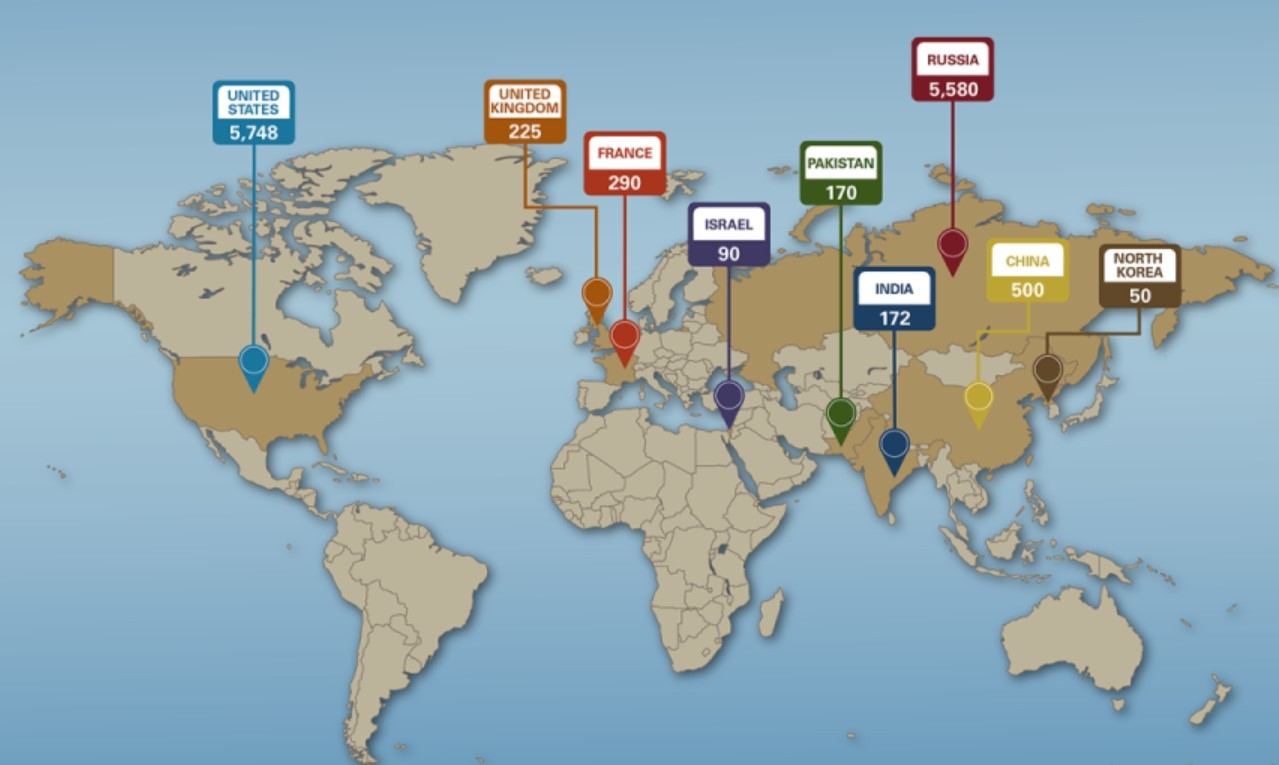
 How Many Countries Are Armed with Nuclear Weapons in 2024/2025? How Many Countries Are Armed with Nuclear Weapons in 2024/2025? |
When did Ukraine Give up Nuclear Weapons?
By May 1992, Ukraine had already evacuated its tactical nuclear weapons, and the country was prepared to hand over its strategic nuclear weapons in exchange for payment and security guarantees from the nuclear powers, namely Russia and the United States. Ukraine and the three nuclear powers—Russia, the US, and the UK—signed the Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances on December 5, 1994.
As a nation that willingly disarmament its nuclear weapons and became a party to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT), Ukraine was assured of its sovereignty and security in this document. Both China and France signed separate declarations endorsing the Memorandum.
 TOS-1: Russia's Most Powerful Non-Nuclear Weapon in Ukraine Battlefield TOS-1: Russia's Most Powerful Non-Nuclear Weapon in Ukraine Battlefield The TOS-1 thermobaric rocket system is said to be one of the "unique" weapons that the Russian military uses on the Ukrainian battlefield. |
 Top 9 Worst Nuclear Disasters of All Time Top 9 Worst Nuclear Disasters of All Time Ukraine was devastated by Chernobyl, the world's worst nuclear accident. There have been numerous nuclear disasters that have caused havoc throughout world history. |
 Top 10 Largest Nuclear Plants In the U.S (2025) Top 10 Largest Nuclear Plants In the U.S (2025) U.S. nuclear power plants generate more electricity than any other country in the world. Take a look at the current ranking, by capacity, of the ... |
 Top 10 Countries Have the Most Nuclear Reactors in the World Top 10 Countries Have the Most Nuclear Reactors in the World On a global scale, 411 reactors were in operation. The question then becomes, which country has more nuclear reactors and is thus considered a nuclear ... |